Linux
The new version of Linux 5.13 comes with enhanced security, support for Apple M1 and more
Linus Torvalds released version 5.13 of the Linux kernel where it provided early support for the new Apple M1 chip with basic support, new security features for Linux 5.13 such as Landlock LSM, Clang CFI support, and the ability to randomize the kernel stack offset on every system call, as well as s Support for HDMI FreeSync and early implementations of Aldebaran, among others.
About 47% of all changes introduced in 5.13 are related to device drivers, about 14% of changes are related to updating code specific to the hardware architecture, 13% are related to the network stack, 5% are related to the file system, and 4% are related to the kernel subsystem internals.
Torvalds called the new version “pretty big”.
“We’ve had a pretty quiet week since rc7, and I see no reason to delay 5.13. The roundup for this week is small, with just 88 uncombined commits (and some of them just rollbacks). Of course, while last week was small and quiet, the 5.13, on the whole, was pretty big. In fact, it is one of the most important versions of 5.x, with over 16,000 commits (more than 17,000 if you count mergers), from over 2,000 developers. But this is a general phenomenon, not a specific phenomenon distinguished by its unusual character,” wrote Torvalds.
Major new features of Linux 5.13
One of the most important new features of the Linux 5.13 kernel is early support for Apple’s M1 chip, where at the moment you only have hardware support and code execution, but a lot of optimization is expected. Graphics acceleration is not yet available, but it is hoped that in the next version initial support will also be available.
Another news presented in Linux 5.13 in relation to security is Landlock, which is a new security module that can run alongside SELinux to better manage processes. It allows to limit interaction with external environment group processes and was developed with a view to isolation mechanisms such as Sandbox, XNU, FreeBSD Capsicum, and OpenBSD Pledge/Unveil.
With the help of Landlock, any processes, including those that are not rooted, can be isolated reliably and avoid going through isolation in case of vulnerabilities or malicious app changes. Landlocks allow processes to create secure sandboxes that are implemented as an additional layer on top of existing system access control mechanisms. For example, a program may deny access to files outside the working directory.
also, improvements to the RISC-V architecture are highlighted, because in this new version support for kexec, crash dumps, kprobe, and kernel launch are implemented in place (execution in place, execution from native media, without copying to RAM).
Also for modern Intel processors, a new cooling controller has been won, Initial support is also provided for this manufacturer’s new system, branded Alder Lake-S (12th generation).
Meanwhile, AMD highlights FreeSync support via HDMI, support for ASSR (Alternative Encoder Seed Reset), ioctl to request video encoding and decoding capabilities, and CONFIG_DRM_AMD_SECURE_DISPLAY mode to detect changes to the screen displaying important information. Support for the ASPM power-saving mechanism has been added.
From other notable changes of this new version of Kernel:
- Support for the Simultaneous Translation Search Buffer Buffer (TLB) feature for some minor performance benefits In fact, Linux 5.13 x86 memory management work provides a small performance optimization which is especially useful given the CPU security mitigations of recent years affecting TLB.
- Support for AMD Zen for Turbostat.
- Loongson 2K1000 bracket.
- KVM provides AMD SEV and Intel SGX upgrades for guest virtual machines.
- Support for Intel bus key detection has been added in addition to existing support for separate key detection.
- KCPUID is a new utility in the tree to help configure new x86 processors.
- A generic USB display driver has been added for settings such as using the Raspberry Pi Zero as a display adapter.
- Support for “Intel DG1 Platform Monitoring Technology” / telemetry platform.
- The POWER9 NVLink 2.0 driver has been removed due to lack of open source user support.
- Direct Rendering Manager driver update.
Linux
2 Easy Ways to Format Flashdisk on Ubuntu Linux, which method do you choose?

Flash format is an activity that aims to empty the files stored in it. This method is done for various reasons, such as wanting to copy new files, removing viruses, and others.
Flash format in Linux is not much different from the flash format in Windows, and it’s just that there are various ways of formatting that you can do. Depending on your understanding of which one is easy, you can use your method.
In this discussion, I will use two of the most common and easy-to-use ways to format a flash drive on Linux, namely how to format a flash drive manually and via the Terminal. The Type of Linux that I use here is the desktop version of Ubuntu 16.04.
How to Format Flashdisk on Linux Ubuntu
( I. ) Format Flash Disk Manually
The one most often used by users is how to format the flash here manually I use. The steps are as follows.
1. Open your file explorer or directory. Click on the flash drive that you want to format to see if your flash drive is legible, what it contains, and are you sure you want to format it.
2. After that, right-click on your flash device, as shown in the picture—Click Format to empty your flash.
3. Next, there are options ( Erase, Type, and Format ) that you can adjust to your needs on this Volume Format. You can follow the default options as shown in the picture.
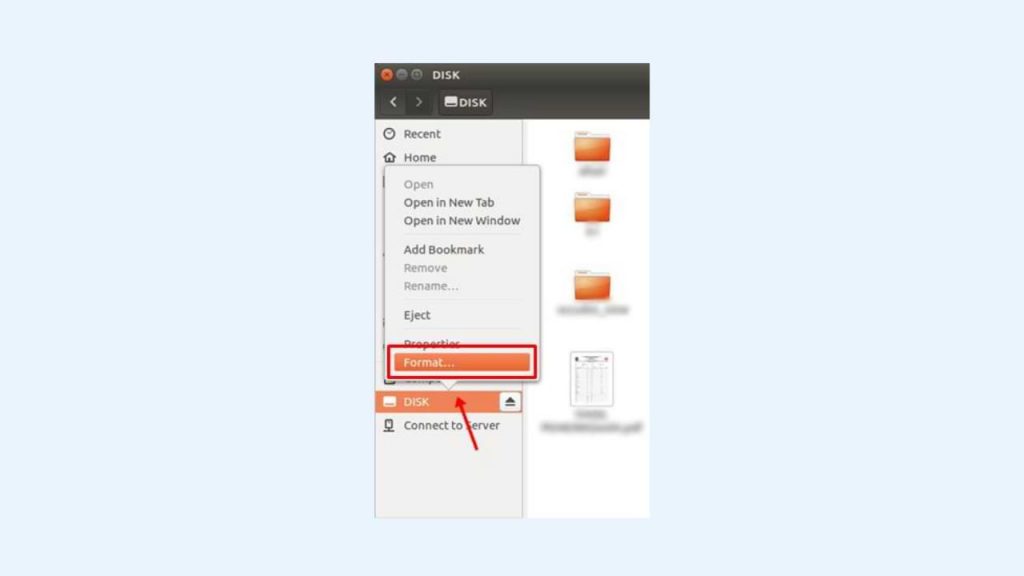
- I select ‘ Don’t overwrite existing data (Quick )’ in the Erase section. This option makes the formatting process faster.
- I choose the FAT format for Type here, but you can select another such as NTFS.
- Then, write a new name for your flash device in the Name field.
- Next, click the Format button.
4. After that, a confirmation will appear again to make sure you do the correct format of the flash. At this stage, the Type of your flash device will be displayed as indicated by the arrow in the image. The flash that I formatted is branded HP and has a capacity of 16GB. Click the Format button to start the flash format process.
5. Format your flash drive has been successful. You can check it by re-opening your flash directory and seeing that the flash drive is empty.
( II. ) Format the flash drive via Terminal.
In addition to manually, you can format the flash via the Terminal. How to? Follow these steps.
1. First, you can check the contents of your flash drive first to make sure you format it. Here, the name of my flash is My FD.
2. Open your Terminal. You can use the shortcut by pressing the keyboard’s Ctrl + Alt + T keys. Type the command:
sudo fdisk -lThe above command aims to find out the address of your flash drive. In the command, use the word sudo, where the Terminal will ask for your password input first. Enter your password; then, the Terminal will display the specifications of the device installed on your computer.
The device that is connected is the flash that we will format. You can ensure the device is your flash drive by observing its size. The example image above says 15.1 G, which means that the flash that I will format is filled with 15.1 GB. Then, remember the address. The address is listed in the Device column, wherein the image above it says /dev/sdb1.
3. Next, use the flash address we know earlier to run the umount command. This command aims to release the flash that is currently associated. You can see the related flash disk in the file explorer, wherein the flash name has an arrow button, as shown below.
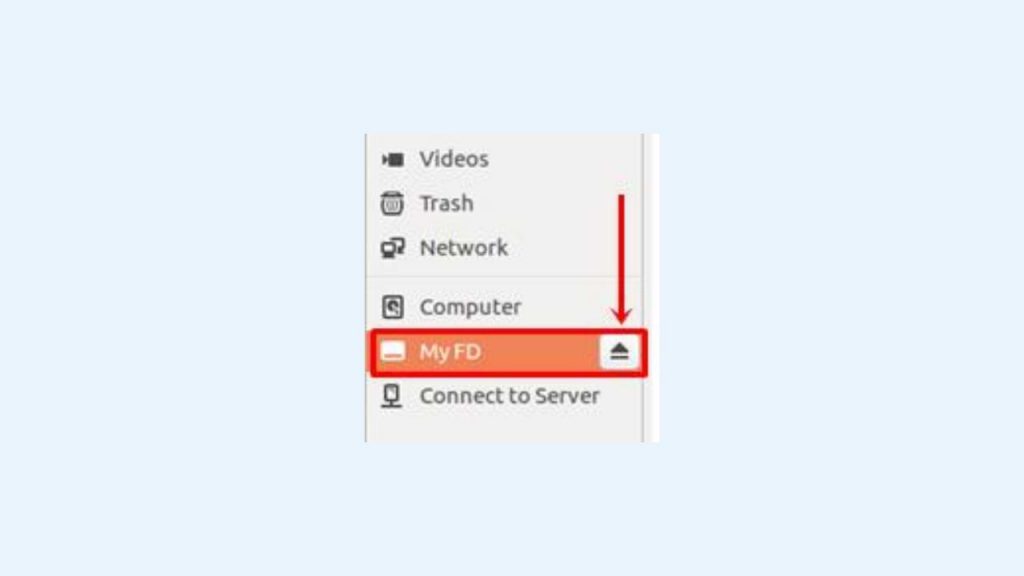
Use the command below to remove your pen drive.
sudo umount /dev/sdb14. Next, you can type a command like the one below to format the flash drive.
sudo mkfs.vfat /dev/sdb1There is the word ‘ vfat ‘ in the command where FAT states the flash format after formatting. You can replace it with NTFS, hfs, ext2, ext3, ext4, and others according to your needs.
5. Finally, your flash is successfully formatted. To check, please open your file explorer and prove your flash drive is empty.
Before formatting the flash drive, make sure there are no important files that will be deleted. Back up your precious data if you are worried about losing your files. That’s how to format the flash on Linux Ubuntu easily. Give your feedback in the comments column below. Thank you.
Linux
How to Install Microsoft Teams on Linux

For those who don’t know, Microsoft Teams is now available as a Multi-Platform application on almost all operating systems, be it Windows, Mac, Linux, Android or iOS.
Now about this, we will summarize the short steps on how to Install Microsoft Teams on Linux. As usual, here, I will use Elementary OS as my mainstay Linux OS.
Here are the short steps.
Step 1. First, please open the Microsoft Teams site.
Step 2. Please download the Installer file from Microsoft Teams; please adjust it to the Linux distro you have, DEB for Ubuntu, Debian and all their descendants, and RPM for Fedora, CentOS and all their siblings.
Step 3. After the file is downloaded, please open the file, and if your Linux already has an app installer, the steps will be easier because we click install.
But if it doesn’t exist, we can use the classic steps by using Terminal. Open Terminal > Go to Directory Download > Then type the following command:
sudo dpkg -i <namafileinstaller>Exactly as in the picture above, after typing the command, you need to enter your root password, and then the installation will run until the Microsoft Teams application is installed.
Well, please try, guys; it’s easy, isn’t it? I hope this article is useful.
Linux
GParted, Partition Management Application for Linux Operating System
Have you ever heard of GParted? This name may still sound less familiar to your ears, especially for those who use the Windows operating system because GParted is intended for Linux users.
Although it sounds less familiar, this application is quite a lot of people who use it. One of the reasons is because GParted offers ease of operation. Even people new to using it tend not to experience complicated problems even though it is the first time they try it.
What Are the Features of GParted?
GParted is an application that can run on both x86 and x64 computers with operating systems such as Windows, Mac OS, and Linux with a minimum RAM size of 256 MB. From these specifications, we can know that this application is light because it only requires a RAM capacity of only 256 MB.
Some of the features that make GParted one we recommend include:
- Create or delete partitions
- Format partition
- Resize partition
- Mounting and unmounting partitions _
- Label
- Checking storage conditions
- Enable and disable Swap (this feature can be used on devices with Linux OS)
- New UUID
- and others
You can use all of these features according to your needs. Using the features in GParted is not too difficult because the instructions are clear. Also, because GParted is GUI, it makes the instructions easy to understand.
How to Use GParted
- As usual, you download the GParted application.
- There will be an ISO file; then, you burn the file.
- Restart the computer and make sure that the boot CD-ROM is in the first place
- GParted is ready for you to use
- You can click Resize or Move if you want to adjust the size of the hard disk.
- You drag across the partition towards the left. Don’t forget to pay attention to the words New Size to create a new size and Free Space Following, the new partition you are using.
- Then you press the Resize or Move button to start this process
- You click the new partition in the Filesystem section. Then select ext3 and label ‘/.”
- Click the Add button, then apply to begin the partition change process.
- Restart the computer and see the size of the partition on the hard drive now
- Don’t forget to backup your data first before using GParted.
For your information, several versions of the Linux operating system that can use GParted include Fedora, Ubuntu, Debian, and Open Suse. GParted stands for Gnome Partition Editor, an application with a GUI or Graphic User Interface.
This application is used for storage management, namely SSD or hard disk. Functions of GParted as found in the Partition Wizard in DLC Boot for Windows OS. At the beginning of its creation, this application was intended for Linux OS.
However, now you can download GParted and use it for Windows OS. By using this application, you can edit, resize, or create or delete partitions on the storage media on your computer or laptop.
-

 Phones5 years ago
Phones5 years agoApple iPhone 11 (2019) – Release, Info, Leaks, Rumors
-
![Huawei's New Operating System is HarmonyOS [ Officially ],harmony os,huawei new operating system, huawei harmony OS,](https://www.thedigitnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/Screenshot__2285_-removebg-preview-2-1-400x240.png)
![Huawei's New Operating System is HarmonyOS [ Officially ],harmony os,huawei new operating system, huawei harmony OS,](https://www.thedigitnews.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/Screenshot__2285_-removebg-preview-2-1-80x80.png) Phones5 years ago
Phones5 years agoHuawei New Operating System is HarmonyOS [ Officially ]
-

 News5 years ago
News5 years agoBelle Delphine bath water – Instagram Model Sells Used Bathwater For 30$ To Their Loyal Followers
-

 Tech5 years ago
Tech5 years agoLevi’s Bluetooth Jacket Lets You Control Your Smartphone